How to Get Featured in Google’s AI Overviews: A Guide to the New SEO
- September 4, 2025
- SEO Snapshots
💡 Quick Answer:
To get featured in Google’s AI Overviews, create semantically rich, structured content that clearly answers user questions in a conversational format. Use schema markup, reinforce E-E-A-T, optimize for passage ranking, and align your page structure with natural search intent. Your content should feel like the answer—not just an article.
Summary: Google’s AI Overviews, part of the Search Generative Experience (SGE), are transforming search by replacing traditional link-based results with AI-powered summaries. This guide helps SEO professionals and content creators adapt by focusing on the strategies that matter most—semantic SEO, entity optimization, Core Web Vitals, and E-E-A-T. From authorship and structured data to passage targeting and conversational tone, you’ll learn how to future-proof your SEO and earn visibility in AI-powered SERPs.
Google’s AI Overviews, officially rolled out in 2024 as part of the Search Generative Experience (SGE), are actively redefining how users interact with search result pages. These AI-generated summaries, powered by Google’s Gemini language model, synthesize information from multiple sources across the web to deliver direct, concise answers within the SERP itself.
This shift introduces a new dynamic to organic visibility. Where traditional SEO aimed to secure blue-link rankings, AI Overviews now prioritize contextually rich and factually authoritative content to feed their summaries. As a result, generating traffic isn’t just about being indexed — it’s about being interpreted and quoted by Google’s generative AI layer.
To maintain relevance — and earn digital real estate at the top of the funnel — marketers and content strategists must rethink their approach. AI-optimized content demands precision, credibility, and structure that aligns with how language models parse and present information. Ready to take control of your search presence in this emerging terrain?
Decoding Google’s AI Overviews: A New Layer in Search
What Exactly Is an AI Overview?
AI Overviews are generative summaries created by Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE). These overviews appear at the top of some search engine result pages and provide multi-sentence, synthesized answers to user queries. Unlike traditional snippets that pull exact fragments from a single URL, AI Overviews aggregate and rephrase content from multiple indexed sources to deliver a more comprehensive response.
They reflect Google’s move toward conversational, context-aware information delivery. Instead of featuring short, source-attributed quotes, AI Overviews often resemble an expert-written paragraph answering the query holistically. The goal: reduce the need for multiple clicks by offering cohesive conversational insights directly in the SERP.
How Do They Differ from Featured Snippets and Answer Boxes?
Featured Snippets typically extract verbatim text from a designated source and display it in a single block of content, often accompanied by a link and image. Answer Boxes, on the other hand, usually show factual, structured data—dates, figures, definitions—relying on Google's Knowledge Graph or authoritative data sources.
AI Overviews diverge from both. Rather than quoting content directly, they paraphrase and interpret. The text generated doesn't always map to exact phrases on the source pages. They also draw from a broader array of materials, rather than highlighting a single primary site. That shift has implications for attribution, traffic, and authority.
What Happens to Source Links?
Source attribution within AI Overviews is both present and diffuse. Google cites sources with clickable links, but not always for every sentence. Typically, these links appear underneath the overview as a list of cited websites, denoted by a “Show more” dropdown or a “Sources” heading. Users must consciously engage with this feature to discover referral links.
This model reduces guaranteed visibility. Being referenced doesn’t ensure front-and-center placement like in a featured snippet. However, it still signals trust and relevance in Google's assessment, which can indirectly influence traffic, brand recognition, and long-term rankings.
- Traditional Featured Snippets: Single-source, word-for-word excerpts with clear attribution.
- Answer Boxes: Data-driven, often devoid of source links, pulled from Google’s own knowledge base.
- AI Overviews: Multi-source, AI-generated text with generalized attribution via discrete citations.
Search results powered by SGE reveal their AI origin explicitly, often labeled with “AI Overview” and featuring distinct visual formatting. As of early 2024, these outputs are still evolving, but Google has steadily expanded their presence, particularly for complex, multi-part queries.
* Content Update 9-04-25
🔥 Suggested Blog Insert (Freshness Update — September 2025):
[NEW] Proven AI SEO Strategies Backed by Research (September 2025 Update)
A comprehensive meta-analysis of 19 research papers and 6 real-world case studies—conducted by Organic Labs, iPullRank, and top SEO leaders—has uncovered what actually works for ranking in AI Overviews (AIOs) across Google, ChatGPT, and Perplexity.
Key Takeaways from the 10,000+ LLM Responses Analyzed:
| Strategy | Correlation with AIO Inclusion |
|---|---|
| ✅ Structured Content (FAQs, Lists, Schema) | 0.81 |
| ✅ Long-Form, Comprehensive Content | 0.79 |
| ✅ Brand Mentions / Digital PR | 0.76 |
| ✅ E-E-A-T Signals (bios, expertise) | 0.64 |
| ✅ User-Generated Content / Reddit / Quora | 0.54 |
| ✅ Entity Presence in Wikidata/Wikipedia | 0.49 |
| ✅ Reviews & Reputation Signals (G2, Trustpilot) | 0.44 |
| ✅ Bing Indexing & Recency | 0.42 |
| ⚠️ Prompt Injection (Experimental) | 0.17 (low, not recommended) |
What This Means for You:
Focus on structured content (FAQPage, HowTo schema) + semantic clarity
Invest in comprehensive hub pages (2,000+ words) covering entire topic clusters
Layer in off-site brand mentions, Reddit discussions, and authoritative reviews
Ensure you're indexed in Bing (87% of ChatGPT citations come from Bing’s Top 10!)
✅ For a full strategy checklist, download our AI Overview Optimization Guide (PDF)
🔗 Source: Optimizing for AI Search: Meta-Analysis of 19 Studies
Why SEO Specialists Should Prioritize Google’s AI Overviews
AI Overviews Aren’t Just A New Feature—They’re A Fundamental Change
Google’s AI Overviews have upended the traditional SERP model. Instead of relying on a single page ranking first, the search engine now synthesizes insights from multiple sources to answer user queries in AI-generated summaries. For SEO professionals, this shift moves the target. The new benchmark isn't just visibility on the first page—it’s extraction and inclusion within Google’s own curated response.
Visibility Now Depends on Inclusion, Not Just Ranking
Historically, SEO focused on ranking in the top three organic results, with position one as the holy grail. AI Overviews dilute that value. Google’s AI might pull content from position six, page two, or even a site you’ve never heard of—so long as it satisfies relevance, depth, and context criteria. This changes how authority and relevance are interpreted.
Ranking first doesn’t mean anything if your content isn’t used as source material in the summary block. Sites that appear in the AI Overview gain instant authority in the eyes of users who never scroll down to organic listings. It’s a new kind of zero-click dominance, one that bypasses the traditional click-through hierarchy entirely.
Authority Signals Are Evolving—Fast
Inclusion in an AI-generated overview broadcasts trust. Google’s selection implies that your site aligns with its interpretation of authoritative and factual information. For a brand or publisher, this can translate into:
- Improved topical authority—being cited repeatedly signals domain expertise to the algorithm.
- Indirect traffic boosts—users frequently reverse-search sources listed in overviews.
- Increased brand visibility—appearing in AI outputs makes your site part of the new default user experience.
Rather than fighting for position-based dominance, SEO specialists are now contending for relevance in a dynamic, context-driven content model. The only way to win? Understand what makes content extractable, attributable, and trustworthy from an AI’s perspective.
Semantic SEO: Building the Context AI Needs
What Semantic SEO Really Means
Semantic SEO focuses on meaning, not just keywords. It enhances a search engine’s ability to understand user intent and the contextual relationships between concepts, entities, and their attributes. Traditional keyword matching no longer satisfies Google's evolving AI models, especially in the age of AI Overviews. Language models prioritize contextual depth and semantic connectivity over simple word matching.
Instead of writing separate pages for each keyword variation, semantic SEO weaves together concepts that hold meaningful relationships. This creates a comprehensive, interconnected narrative around a topic—fuel for generative AI like the one driving AI Overviews.
Using Semantic Relationships to Establish Topical Authority
Topical authority doesn’t come from keyword density. It derives from how deeply and accurately content explores a subject, incorporating semantically related terms and structured narratives that mirror how information is interconnected in knowledge graphs.
- Include related terms, synonyms, and conceptually connected ideas. For example, if you're writing about climate change policy, naturally introduce related concepts like carbon credits, emission trading systems, and Paris Agreement targets.
- Layer information hierarchically: use headers, subheaders, and structured outlines to reflect semantic proximity. A section discussing renewable energy incentives will logically follow one about governmental strategies, reinforcing relational understanding.
- Avoid keyword stuffing. Instead, build thematic clusters that show the full picture around your core topic.
Mapping Entities and Concepts in Your Content
AI Overviews don’t summarize isolated keywords. They synthesize across knowledge domains built from entities—people, places, things—and how those entities connect to broader concepts.
- Identify core entities in your content, such as organizations, products, industries, or public figures, and represent them accurately and contextually. Google's Knowledge Graph uses these entities as anchors for summary generation.
- Use co-occurrence patterns. If a topic frequently appears near another in trusted sources (e.g., machine learning and predictive analytics), reflect that connection in your articles.
- Position your content to answer not just "what," but "how" and "why." Explain the role of each entity within the larger system you're covering.
Semantic SEO transforms flat content into a dynamic network of ideas. That network is what generative AI taps into to build reliable, answer-rich overviews. Want to evaluate how well your pages define and connect core concepts? Try this: Can your content stand as an explainer even without direct keyword queries?
Entity Optimization for AI Understanding
Why Entities Drive Google’s Comprehension Models
Google’s AI Overviews don’t retrieve web pages the way traditional search once did—they synthesize facts. To do that, the system relies on an entity-based understanding of the content. Entities—such as people, organizations, places, events, or clearly defined concepts—anchor the relevance model in the Knowledge Graph and help the AI distinguish context, disambiguate terms, and assess confidence levels.
When Google parses a page, it identifies named entities and maps them to known nodes in its Knowledge Graph. Each mapped entity adds to the perceived topical precision and helps Google resolve what the content is about. Pages linking back clearly to existing structured data get more traction in this model. If your page uses consistent, authoritative mentions of recognized entities, Google’s AI can assign relevance faster and more confidently.
How to Optimize for Entities in Your Content
- Target known entities Integrate references to real-world subjects that already exist in Google’s structured database. Think major brands, locations with Wikipedia entries, public figures, or industry-specific concepts like “enterprise resource planning” or “GraphQL.”
- Establish an entity-first structure Rewrite or structure content so the primary subject—the entity—is clear in the introduction and reinforced throughout. Ask: Who or what is this page about? Then surface that answer quickly using H1s, subheadings, and contextual links.
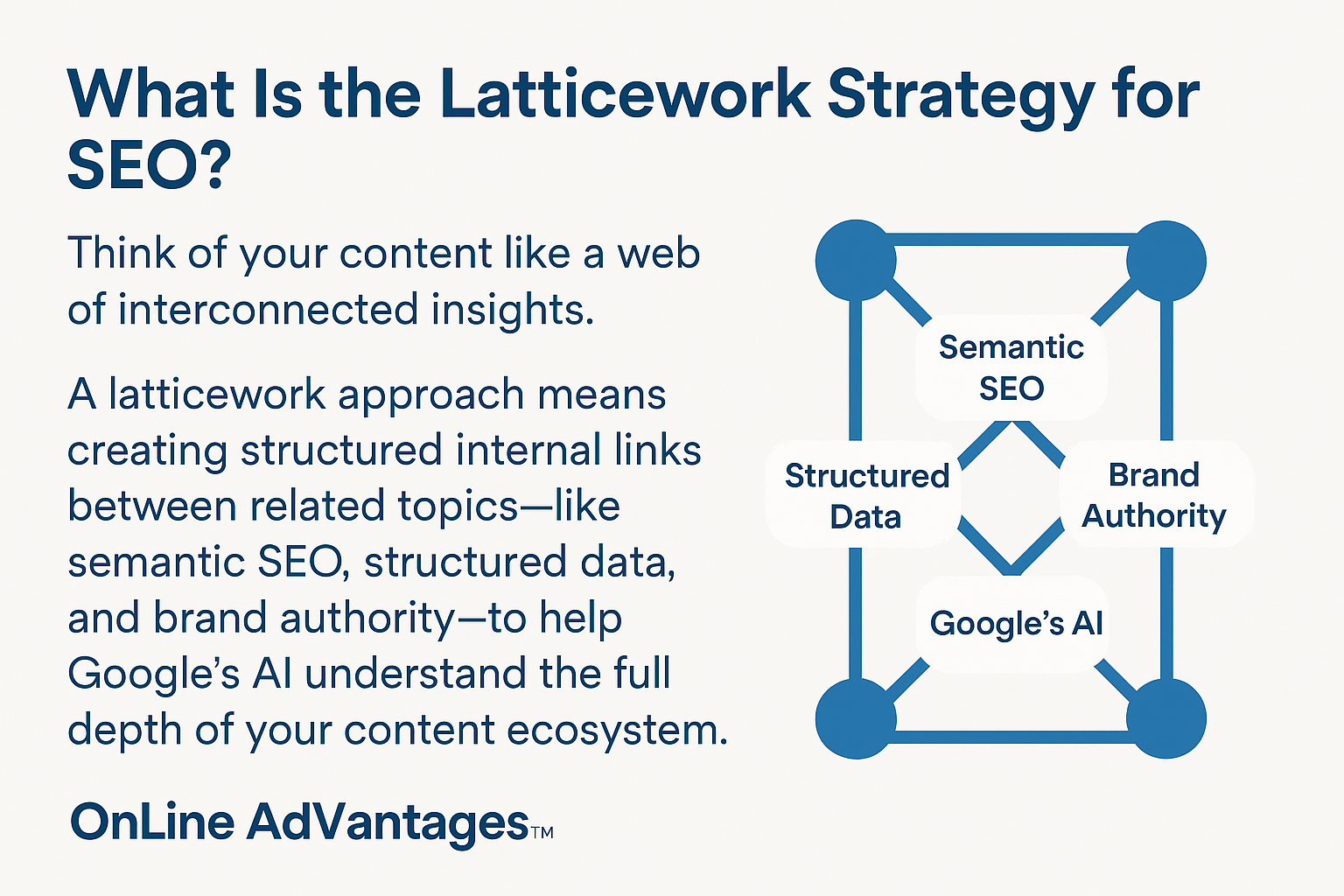
- Embed semantic proximity Anchor new entities in relation to known ones. Instead of writing “our tool uses advanced algorithms,” say “our AI tool—built on top of OpenAI’s GPT-4 API—uses reinforcement learning algorithms.” This gives Google semantic latticework to triangulate meanings.
- Use structured internal linking around entities Connect mentions of your primary entities to other relevant pages within your site. If your article references “Inbound Marketing,” and you have a glossary or guide about it, link to that. Do this contextually—not in navigation bars, but within paragraphs—to signify topical clusters.
Latent Relationships Add Weight
Google also measures implicit interconnections between entities. If your site consistently links content about "Boston Dynamics" with robotics applications, AI ethics, and warehouse automation, it signals authority across those related verticals. This builds what Google's documentation has previously described as a “web of knowledge,” increasing your odds of being cited in an AI Overview.
Have you audited your content for core entities recently? Try pasting a few paragraphs into Google’s NLP API demo. Which entities are detected—and more importantly, which ones are missing? Adjusting content for clearer semantic connections can shift your visibility from dataset margins to AI Summary citation status.
Deep Relevance Wins: Matching AI Overview Expectations
Why Surface-Level Content Fails
Google’s AI Overviews no longer tolerate vague, unfocused pages. The system filters for content that directly reflects a user’s search intent—instructure, scope, and semantic coverage. Pages that scrape the surface with loosely related ideas, or attempt relevance through keyword repetition, consistently fall short. Topical precision and information richness move your content into AI territory where results matter.
What Comprehensive Content Looks Like
To secure a place in AI Overviews, your content must present as definitive. That means it answers the core query entirely, anticipates logical follow-up questions, and solves for what the user is expecting to learn or decide.
- Coverage of Core + Secondary Intents: Start by dissecting the central query. Define its dimensions—informational, navigational, transactional—and then expand contextually. For example, a page on "organic fertilizer benefits" should also touch on soil improvement, plant-specific advantages, and common application mistakes.
- Incorporate Follow-Up Questions Naturally: If a user asks “How to optimize for AI Overviews,” they may also be wondering, “What factors influence inclusion?” or “How does Google evaluate relevance?” Address them inline with strong subtopics.
- Emphasize Topical Depth over Repetition: Instead of reiterating exact-match phrases, use semantically related concepts. A piece about “budget-friendly electric bikes” should unfold into comparisons, battery range analysis, maintenance tips, and price-performance evaluations.
Align with Google’s Understanding of Authority
AI Overviews score relevance by comparing your content against known high-authority corpora. To match that depth:
- Include data, citations, or original examples to anchor trust.
- Integrate terminology that aligns with expert language in the field, avoiding oversimplification.
- Build around entities and relationships, not just phrases—Google connects ideas, not just words.
Are You Really Answering the Question?
Pull up your last blog post or landing page and ask: Does this piece cover all dimensions of the query, or does it leave the user with more questions than answers? Because Google’s AI doesn’t just scan for answers—it promotes content that preempts needs, resolves uncertainty, and satisfies curiosity in one scroll.
Structured Data and Schema Markup: Communicating with AI
Search engines rely on structured data to interpret content with greater precision, and Google’s AI Overviews multiply that reliance. Schema markup acts as a signal booster, enabling crawlers to parse not only what your page says—but what it means. When correctly implemented, structured data accelerates comprehension and increases the likelihood of your content being selected for rich presentations in AI-driven results.
What Schema Markup Does for AI Overviews
Google uses schema to contextualize entities, relationships, and actions within a page. When underlying structure clearly defines what a page is about—who the author is, what the article explains, how a product functions—AI systems can convert that clarity into high-surface visibility.
For AI Overviews, clean and consistent schema helps the model:
- Understand the topical density and thematic hierarchy of your content.
- Verify the credibility of the source by evaluating authorship and domain reputation via structured signals.
- Extract dynamic answers from HowTo and FAQ markup for inclusion in structured or conversational summaries.
Essential Schema Types for AI-Friendly Pages
Several JSON-LD schemas produce tangible benefits under Google's NLP-focused indexing and ranking systems. Here’s where to start:
- FAQPage: Aligns exceptionally well with multidimensional intent queries that Google surfaces via its generative AI.
- HowTo: Allows models to identify step-by-step tutorials, increasing the semantic utility of instructional content.
- Article: Clarifies content type, datePublished, headline structure, and publisher details—key metadata used to evaluate clarity and authority.
- Person & Organization: Reinforces author credentials and brand legitimacy, supporting Google’s trust signals for E-E-A-T.
- Review & Product: Defines user-generated content, aggregate ratings, and product specifications—ideal for commerce-relevant search queries.
Reinforcing E-E-A-T Through Structured Authorship
AI Overviews weigh authorship when selecting content for surfacing. Using the Person and Organization schema types, you can specify qualifications, affiliations, and social validation elements. Properly structured, this data supports the "Experience" and "Expertise" elements of Google's ranking systems.
Include fields such as name, sameAs (linked profiles), jobTitle, and alumniOf for individuals. For organizations, use founder, url, and logo to build out a credible data graph.
Validation: Non-Negotiable
Markup errors can nullify all structured data benefits. Use Google's Rich Results Testing Tool to check for compliance and output visibility. This tool highlights issues in the JSON-LD and previews how your structured data may display—use it consistently during content deployment.
Schema isn’t optional in the AI era. It now functions as language, metadata, and verification in one, directly impacting how your content is interpreted and ranked by large language models.
E-E-A-T as a Baseline for Trustworthiness
Google’s AI Overviews don’t guess. They synthesize responses from content that meets a high standard of trust, relevance, and accuracy. At the core lies E-E-A-T: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. These signals filter sources, spotlighting those viewed as reliable by Google's systems. Content lacking in E-E-A-T simply won’t feature—no matter how well optimized the metadata or structured data may be.
Strengthening E-E-A-T: Practical Implementation
Rather than treating E-E-A-T as abstract theory, fold it directly into your production and publishing workflows. Each part plays a distinct role, and together, they shape Google's judgment about your site’s credibility.
- Showcase Authors’ Credentials Identify who wrote the content. Link to detailed author bio pages. Provide verifiable qualifications, certifications, or roles that establish expertise. For example, a medical article authored by a board-certified physician should clearly state that affiliation, ideally linking to the author's professional profile or licensure registry. Don’t allow ghostwritten content to mask your authority signal—Google detects this pattern.
- Incorporate Experience-Backed Insights Reflect personal or organizational experience. First-hand accounts, demonstrated know-how, and operational knowledge all serve as strong indicators of credibility. Include real-world case studies, personal test data, process documentation, or behind-the-scenes decision-making. These markers differentiate expert commentary from generic aggregates and help anchor your content in situational reality.
- Build Authoritativeness with External Validation Secure coverage, mentions, or citations from established entities in your niche. This might include academic citations, media features, government linkbacks, or references from industry-leading publications. Aim for links and brand mentions that demonstrate peer recognition. Pages cited by respected third-party sites carry clear authority signals; Google’s AI models reward this by surfacing them in Overviews.
Each piece of content functions as both an information source and a reflection of the site’s broader reputation. There’s no shortcut around E-E-A-T—it's the entry ticket for inclusion in AI-processed summaries.
Writing for Real Conversations: Optimizing Content for Natural Language Queries
Why Google’s AI Overviews Favor Conversational Language
Google’s AI Overviews don’t just parse keywords—they understand intent. That shift prioritizes content that reads the way people speak. When users ask, “How do I fix a leaky showerhead?” they expect an answer structured like an actual reply, not a textbook fragment. AI Overviews are built to identify and surface content that mimics these natural patterns.
Since the launch of AI Overviews, content that uses clear, colloquial phrasing consistently ranks higher. This doesn’t mean dumbing things down. Rather, it means anticipating how people frame questions and delivering answers in plain, structured language.
Rewriting Content to Match User-Speak
AI Overviews recognize patterns common in natural conversation. Adapting your content to this format requires more than tone—it requires structural adjustments. A few proven tactics make the difference.
- Implement question-based headers: Think like a user. Instead of titling a section “Optimal Planting Techniques,” reframe it as “What’s the best way to plant tomatoes in raised beds?”
- Craft straight answers right after the question: Use a first-sentence summary that immediately satisfies the query. Don’t bury the lead.
- Incorporate clarifying sub-questions: After answering one question, anticipate the logical follow-up. Answer it before users need to leave your site to find out.
Dialogue-Centric Tone in Practice
Here’s the shift: from declarative and dense, to conversational and fluid. Instead of writing, “Tomatoes grow optimally in soil with a pH of 6.0–6.8…” start with what people are actually searching.
- Search-style phrasing: “What kind of soil do tomatoes need to grow?” becomes the H3.
- Immediate answer: “Tomatoes grow best in slightly acidic soil—that means a pH between 6.0 and 6.8.”
- Follow-up suggestion: “Not sure how to test soil pH? Here’s a simple method using a basic kit you can buy online.”
Mimicking Conversational Intent Structurally
To mirror real inquiry structure, use headers that reflect long-tail or voice search queries. Test your titles against how someone might ask Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant for help. “How do I update my iPhone without deleting apps?” or “What’s the difference between WiFi 5 and WiFi 6?”
These aren’t just tips—they align your content with how Google parses and ranks conversational intent. Any section that answers a common question should start with the question itself, serve a plainspoken answer, and follow with briefly elaborated context.
Zeroing in on Long-Tail Phrases
Long-tail queries often carry high intent. Here’s where your content can shine above generic articles. Instead of optimizing for “best running shoes,” write as if you’re responding on a forum:
- Header: “What are the best running shoes for flat feet in hot weather?”
- Opening line: “If you’ve got flat feet and you’re training through the summer, look for shoes with arch support and breathable mesh—models like the Brooks Adrenaline GTS 22 are tailored for both.”
These structures hook Google's semantic understanding and pass straight through to AI Overviews. Because they replicate human dialogue more than robotic text, they’re selected more often.
User Intent Optimization: Aligning with Search Goals
Segment Search Intent Before You Write
Understanding exactly what a user wants when they type a query is fundamental to securing visibility in Google's AI Overviews. Every query roughly aligns with one of three categories:
- Informational intent: The user seeks knowledge or specific facts. These queries often start with "what is," "how does," or "why."
- Navigational intent: The user is looking for a particular website or platform. Think queries like "YouTube login" or "Nike store locator."
- Transactional intent: The user is ready to take action — buy, download, book, or subscribe. Examples include "best budget laptops 2024" or "sign up for Canva Pro."
Content that lands in AI Overviews mirrors this structure. Google's large language models predict what a user is trying to accomplish and surface responses aligned to that goal. When content meets that expected intent clearly and directly, it earns the edge.
Format for the Query, Not Just the Topic
The structure of your content should serve the likely aim behind the query. AI Overviews do not rely solely on keyword matching — they prioritize structure, clarity, and alignment with the type of information sought.
- “Best” or comparative queries: Use ranked lists, preferably numbered, to aid clarity and provide candidates for bullet-rendered AI summaries.
- “How to” or tutorial searches: Structure your content as step-by-step instructional guides. Break down each stage with clear subheadings and logical progressions. AI Overview models favor this clean hierarchy.
- “What is” or definition-focused queries: Start with one sharp, simple sentence delivering the definition. Follow up with contextual elaboration and examples. AI rendering often pulls directly from these leads.
Take a query like “how to consolidate credit card debt”. A high-performing AI Overview excerpt walks through numbered or bullet-pointed steps, starting with evaluating one’s balances and ending with executing the chosen method (e.g., balance transfer, debt consolidation loan). By anticipating that structure and reproducing it with clarity, your content signals relevance to Google's AI systems.
Let Search Behavior Drive Editorial Direction
High-intent alignment isn't guesswork. Use tools like Google Search Console, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to analyze which queries drive impressions for your pages. Then, identify mismatches where pages rank but don't match user goals precisely. Tuning the content format to fit observed intent will boost AI Overview eligibility.
Want to test alignment? Enter your core keywords into Google and observe how the AI Overview answers. Are you mimicking the structure shown? Are your pages solving the same intent with comparable depth?
When you start designing content around intent patterns — not topics alone — you unlock the framework for AI Overview positioning. Format follows function, and function follows user goals.
Mastering Passage Ranking and Microtargeting for Google’s AI Snippets
Google’s AI Overviews don’t summarize entire pages—they extract precise passages that answer queries at a granular level. This shift demands a focused approach to content architecture. Once a strong topical foundation exists, refining how individual blocks of information are framed and delivered will determine eligibility for inclusion in AI-generated results.
How Google Retrieves Passages
Since the December 2020 introduction of passage-based indexing, Google evaluates not only whole pages but also semantically coherent sections within them. BERT and other natural language processing models allow the system to isolate specific paragraphs that best satisfy a nuanced search intent—even from pages not fully optimized on the macro level.
This is not about ranking the entire page higher. The algorithm identifies relevant segments, matches them against query embeddings, and surfaces only those that maximize response precision based on topical alignment and clarity.
Strategic Structuring: Feed the AI the Right Pieces
To get parsed correctly and surfaced in AI snippets, long-form content must guide both human readers and machine systems through a logic tree of inquiry. Here’s how to do that effectively:
- Use question-based subheadings: Frame H2s and H3s as direct answers to known or anticipated queries. For example, instead of “Benefits of Schema,” write “How Does Schema Help AI Understand My Content?”
- Keep paragraphs concise and contained: Limit each block of text to a single central idea expressed within 2–4 sentences. This containment increases the chances of standalone value.
- Insert list formats to break down complexity: Bulleted or numbered lists distill information efficiently. Google’s AI models pull these frequently to capture step-based or comparative insights.
Microtargeting Within Comprehensive Content
Long content should never be monolithic. Each section must microtarget distinct user intents while preserving the macro context. That means multiple searchable touchpoints across a single piece. A 2,000-word article can host 10–15 passage candidates if structured correctly—with each addressing a different sub-intent of the master query.
How many of your content’s paragraphs would stand on their own as a SERP answer? That’s the benchmark Google is now using. Auditing old content for retrievable passage strength and engineering new articles to multiply those points of entry will produce measurable gains—especially in competitive topic clusters where AI Overviews dominate visibility.
Rich Snippets, Featured Snippets, and AI Overlap
Where Traditional Snippets Meet AI-Driven Summaries
Before Google's AI Overviews, the landscape of SERPs revolved around structured HTML content competing for rich snippets and featured snippets. These formats, especially featured snippets — the so-called “position zero” — gave visibility to sites with succinct, well-organized answers to specific queries. Rich snippets, meanwhile, enhanced listings with additional detail like ratings, pricing, duration, and other metadata through structured markup.
Now, AI Overviews have changed the rules, but not completely. Content designed for winning traditional snippets still performs better in AI-generated summaries. The structure, clarity, and schema implementation that power featured snippets directly feed the AI’s ability to extract usable insights. Google uses these same underlying structures to synthesize summaries within AI Overviews, drawing from content with clearly signposted information.
What the AI Is Looking For — And Why Snippet Formatting Still Matters
AI Overviews don’t randomly generate summaries from the web. They source from content that’s already understood semantically and structurally. Typically, that’s the kind of content already earning spots as featured or rich snippets. Here's why that matters:
- Clear headers and subheaders: These help the AI identify topic segmentation, making it easier to pull discrete answers to complex queries.
- Bullet points and numbered lists: Lists offer digestible formats that work well in both traditional snippets and AI Overviews.
- Marked-up semantic data: Referencing schema.org vocabulary through JSON-LD or Microdata enhances machine readability.
- Concise, factual statements: Snippets that win are rarely flowery; they answer the query directly. AI Overviews prioritize this same structure.
Featured Snippets as Training Ground for AI
Google continues to train its language models using web documents that earned high utility across users. Featured snippets offer a proven dataset — user-endorsed content that has fulfilled intent in SERP contexts over time. If a page is consistently pulled into featured snippets, it signals to the AI that this content has both semantic clarity and user validation. Pages optimized for that structure already align with what Google's models prioritize in generating AI Overviews.
This crossover means that investing in the mechanics of traditional SEO — schema usage, concise Q&A structures, topical hierarchy — doubles as an AI Overview strategy. Want to win in AI summaries? Start by dominating rich and featured snippets.
Core Web Vitals and Page Experience Still Matter
High-performing, user-friendly pages consistently surface in Google's AI Overviews. They're not just ranking because of content relevance—they meet the performance benchmarks Google uses to evaluate page experience. This includes metrics quantified by Core Web Vitals and enhanced by overall UX signals.
Google's Core Web Vitals: The Technical Foundations
Core Web Vitals are three specific metrics:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance. Pages should load main content within 2.5 seconds.
- First Input Delay (FID): Assesses interactivity. Interactions should register in less than 100 milliseconds. Note: FID is being replaced by Interaction to Next Paint (INP) in March 2024.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Evaluates visual stability. Pages must maintain a CLS score under 0.1 to minimize layout shifts.
Pages that pass these metrics are more likely to be pulled into AI Overviews as sources because they offer consistent speed, responsiveness, and reliability across devices.
Experience Signals Beyond the Vitals
In addition to the core metrics, Google incorporates broader page experience signals. These include:
- Mobile-friendliness: Responsive design ensures optimal viewing across screen sizes, reducing friction.
- HTTPS Security: Pages served over HTTPS give confidence to users and meet baseline security standards.
- No intrusive interstitials: Overlays that block content create friction and may suppress visibility in AI-selected outputs.
Engagement Metrics: Bounce Rate Is a Signal
AI Overviews respond to behavioral indicators showing that a page solves a user’s query. Bounce rate, while not a direct ranking factor, acts as a proxy for satisfaction. A high bounce rate on short-duration sessions signals a disconnect between user intent and page value.
Low bounce rates, longer dwell times, and high click-through interaction with internal links suggest content that satisfies. AI models factor these patterns when choosing which source to highlight in overview summaries.
Optimizing for Page Performance
- Use lazy-loading for below-the-fold images to speed up initial render.
- Compress assets with Brotli or gzip and serve optimized images via WebP.
- Minify CSS and JavaScript; defer non-critical scripts until after user interaction.
- Use a content delivery network (CDN) to reduce latency for global users.
- Audit LCP elements regularly—often it's a large image or video that isolates loading delay.
Want to test how your site scores? Run a real-world URL through PageSpeed Insights or use Lighthouse in Chrome DevTools for detailed Core Web Vitals data and actionable performance improvements.
Performance is not just technical compliance—it's a reputation statement. In the era of AI Overviews, slow and unstable sites get passed over. Speed gets seen.
Get Recognized: Knowledge Panel and Author Authority in Google's AI Landscape
Why Knowledge Graph Prominence Drives Visibility
Google’s AI overviews heavily rely on its Knowledge Graph to assess and present authoritative information. When your brand or name appears as an entity within this graph, your chance of being cited or featured in AI overviews increases. Entities that exist in the Knowledge Graph gain algorithmic advantages—Google treats them as trustworthy reference points for surfacing in-depth insights and summaries.
Creating and reinforcing entity prominence requires a multifaceted approach: from ensuring alignment across public profiles to structuring on-site data that signals identity and notability. The AI isn’t guessing—it’s pulling from indexed information mapped within this knowledge infrastructure.
Steps to Secure a Google Knowledge Panel
- Establish Digital Identity Across High-Authority Channels: If you or your business doesn’t yet trigger a panel, begin by aligning your name or brand consistently across Wikipedia, Crunchbase, LinkedIn, Google Scholar, and social profiles.
- Add or Claim the Panel via Google: Once Google generates a panel, use your verified Google account to claim it. This gives you control over images, descriptions, and links—details the AI will reference.
- Use Organization and Person Schema: Implement
<Organization>or<Person>schema on relevant pages. Include properties likesameAsandknowsAboutto connect your entity to a broader web of knowledge.
Schema + Structured Identity = Recognition
The AI parses websites differently from traditional search crawlers. It isn’t just looking for keywords—it's mapping relationships. Linking structured data with external identity indicators helps the AI validate and surface you as a credible source.
Maintaining a single narrative across all profiles strengthens this signal. For example, if your LinkedIn, website bio, and Wikipedia entry highlight the same area of expertise, AI systems recognize consistency and elevate your profile in overviews tied to that domain.
Author Recognition Matters More Than Ever
Entities aren't just companies—authors are also ranked within the Knowledge Graph. Google attributes credibility to authors who demonstrate deep knowledge across multiple publications. By linking author profile pages, configuring article schema with the author property, and establishing a robust digital footprint connected to your name, you push your expertise into the AI’s reference framework.
Who's the person behind the insight? If the AI can answer this question reliably, your name becomes a source in itself—not just your site.
Creating AI-Ready Content: Step-by-Step Framework
Research: Find What the AI Is Already Surfacing
Effective content starts with strategic question targeting. Begin by identifying rising queries from Google's Search Generative Experience (SGE), the “People Also Ask” section, and tools like AlsoAsked or AnswerThePublic. These platforms expose conversational patterns and layered search intent, revealing the structure Google prefer
- Use SGE query extractors and SERP APIs to monitor AI snapshot triggers.
- Analyze high-frequency co-occurring questions to establish topical authority.
- Look for multi-intent questions (e.g., comparisons, how-to’s, pros and cons) that fuel AI synthesis.
Create: Structure for AI Interpretation
Center your content around semantic clusters, not just keywords. AI Overviews don’t rely solely on keyword matching—they interpret conceptual relationships. Use internal linking to tie entities together and organize your page with clear hierarchy: subtopics, definitions, FAQs, and related scenarios.
- Break content into modular passages answering specific user intents.
- Use natural language subheadings—the kind that mirrors real questions.
- Incorporate entity associations via NLP-friendly phrasing and co-citation techniques.
To further train the AI on your content as a knowledge source, include lists, tables, and comparison blocks where relevant. These structures increase the odds of snippet extraction for AI answers.
Optimize: Convert Content into Machine-Readable Signals
AI Overview visibility hinges on your site communicating clearly with both users and algorithms. Embed JSON-LD structured data—including FAQPage, HowTo, and Product schemas—where appropriate. Beyond markup, your content must meet Web Vitals thresholds to qualify for visibility tiers in AI-fueled SERPs:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) under 2.5 seconds
- FID (First Input Delay) under 100 milliseconds
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) below 0.1
Pair technical optimization with precise author signals, such as sameAs properties linking author profiles to authoritative platforms like LinkedIn or Google Scholar.
Evaluate: Measure Visibility Potential
Monitoring tools calibrated for generative search are essential. Platforms like Surfer SEO and Content Harmony now include AI Overview predictive models. These models show whether your page meets the passage-level requirements for AI inclusion, as well as the likelihood of snippet eligibility based on topic coverage.
- Test your content’s relevance depth with Topic Coverage Scores.
- Run NLP entity extraction to confirm alignment with known topic graphs.
- Check SGE preview indexing—some tools disclose if your page feeds AI responses.
Iterate: Match the Speed of AI Evolution
Google’s AI Overviews shift with query trends, user feedback loops, and model updates. Static content decays quickly in this environment. Instead, build content update cadences into your workflow. Use platforms like ClearScope or MarketMuse to detect intent evolution and emerging co-entities.
What worked three months ago might no longer meet the markup patterns favored in today’s AI extractions. Schedule quarterly refresh cycles, retesting the intent triggers your content satisfies—and keep training it to remain discoverable in AI top-tier responses.
Track Your Presence in Google's AI Overviews: Tools and Resources
Staying visible in a shifting SERP landscape calls for precision monitoring. Google hasn't released a dedicated tool for tracking AI Overview presence, but several platforms have begun integrating support to meet demand. This section outlines how to track inclusion, monitor search behavior, and create an effective feedback loop using available resources.
Keyword Tracking Tools Testing AI Overview Visibility
- SEMRush: Currently piloting SERP features detection for Google's SGE (Search Generative Experience) in beta environments. Users can opt into visibility experiments for select keywords.
- Rank Ranger: Offers some flagging for AI-generated snippets when tracking certain keywords, though coverage remains partial and inconsistent based on vertical.
- Serpstat and BrightEdge: Both are developing modules to identify experimental AI Overview triggers—particularly around branded queries and structured content.
Monitor Branded and Non-Branded Queries Manually
Automated tools aren't always reliable for something as dynamic as AI Overviews. Use incognito browsing across multiple devices and locations to manually track query visibility, especially for:
- Branded searches (Company name, product lines, author names tied to content)
- Long-tail, question-based queries closely aligned with your content
- Trending topical searches that match recent content updates
Switch between desktop and mobile views to detect shifts in AI Overview appearance. Google is experimenting with format based on context, which can vary significantly across platforms.
Feed Insights Back into Your SEO Strategy
A one-directional view limits impact. Push observational data from SERPs into your analytics dashboards. Monitor user behavior following exposure in AI Overviews vs. traditional snippets. Focus on:
- Changes in bounce rate and time on page for pages suspected to appear in AI Overviews
- Entry pages through organic search that saw a traffic spike after major Google updates
- Shifts in click-through from queries with informational vs. transactional intent
Use Google Search Console’s performance reports segmented by page and query impressions. While it won't confirm AI Overview appearances, indirect patterns—like sudden impressions without clicks—can signal inclusion in non-clickable AI summaries.
Ready to go deeper? Build a query log and record observed AI Overview appearances weekly. Organize findings by URL, query type, and display frequency. This baseline gives a reference point for testing future content enhancements or schema adjustments.
The Strategic Weight of Your Site as a Trusted Result Source
Google’s AI Overviews don’t just surface isolated pieces of well-written content. They prioritize sources with a track record—sites that demonstrate authority, credibility, and consistent visibility across the web. Being selected as a result source goes beyond on-page optimizations. It requires demonstrable, external validation of trustworthiness.
Strengthen Off-Site Signals That Influence AI Inclusion
Off-site factors carry measurable influence in determining whether your content qualifies as a source for AI Overviews. These signals, built over time, serve as Google's reference points for topical authority and domain-wide reliability.
- Backlink Profile Quality: High-quality backlinks from domains with strong domain authority (DA) and topical relevance signal to AI systems that your site occupies a respected position in the information ecosystem. A study by Ahrefs revealed that 91% of all pages get zero traffic from Google, mainly due to a lack of backlinks.
- Brand Mentions and Citations: Even unlinked brand mentions in reputable online publications reinforce entity recognition and authority signals. Natural language models factor in this type of contextual validation.
- Publisher Visibility in Topic Clusters: Sites that consistently demonstrate expertise across content clusters on a topic (for instance, multiple articles supporting a common subject) rank higher in topical authority models. This clustering contributes to predictable inclusion as a trustworthy source in AI-generated responses.
Ensure Indexing Health and Site-Wide Crawlability
Google’s AI systems cannot feature what they cannot access. Technical SEO fundamentals directly impact a site's eligibility for extraction as a source in AI Overviews.
- Crawl Depth and Internal Linking: Shallow crawl depth (3 clicks or fewer from the homepage), combined with strategic internal linking, keeps your content within reach of Googlebot’s attention and reinforcement cycles.
- Canonicalization and URL Cleanliness: Proper canonical tags and consistent URL structures prevent duplication issues and improve clarity in what Google considers the primary version for each topic.
- Index Coverage Monitoring: Use Google Search Console's coverage report to identify and resolve excluded or soft 404s, which can quietly erase high-value pages from SEO impact zones. Pages not indexed have zero probability of appearing in AI Overviews.
Think of your site as a living endorsement. Trusted sources win visibility because they’ve built a reinforced presence across multiple dimensions—technical, contextual, and reputational. Does your domain operate like one of them?
Future Outlook: The Evolution of SEO in AI-Powered SERPs
Search engine optimization will not remain static in an ecosystem increasingly shaped by generative AI. Google’s AI Overviews introduce a paradigm shift—one where traditional ranking signals operate alongside language model-derived contextualization. This new dynamic changes how content is selected, evaluated, and surfaced in search results.
Large Language Models Will Reframe SEO Priorities
As large language models (LLMs) become deeply embedded in search algorithms, they will influence the ranking process by interpreting meaning rather than just matching keywords. Google's efforts—evident through innovations like MUM and Gemini—center on machines that understand nuance, linguistic relativity, and multidimensional context.
SEOs will need to optimize not just for keywords or links, but for relationships among entities, clarity of semantic structure, and conceptual comprehensiveness. The underlying shift: from keyword density to topic coherence, from backlinks to verified authority, from content volume to informational satisfaction. LLMs can already infer user intent even from vague prompts; content that aligns with their understanding of “best possible answer” will surface more frequently.
Human Insight Will Anchor AI Decision-Making
AI-generated content is spreading fast, but it lacks one critical trait: lived expertise. Google has underscored its preference for human-created, expert-reviewed information. Language models hallucinate; humans validate. For this reason, content tied to credentialed authors, supported by transparent sourcing, and reviewed by specialists will gain precedence across AI Overviews.
Organizations with internal subject matter experts or access to verifiable insights will command stronger trust signals. That content doesn’t just answer the question—it demonstrates real-world authority that AI can detect and elevate. Algorithms will increasingly reward this expertise through confidence scoring and reinforcement learning ranking techniques.
Adaptation Strategies: What's on the Horizon for SEOs
- Editorial refinement will replace keyword stuffing. LLMs identify clarity, completeness, and lexical variation—crisp, in-depth writing will rise above cluttered SEO copy.
- Topic modeling will become essential. SEOs will map content across entities, subtopics, and question clusters to align with how LLMs organize knowledge spaces.
- AI-specific testing tools will emerge. Expect new platforms to simulate AI Overview behavior, giving web publishers insight into how their content performs inside synthesized snapshots.
- Ranking becomes multidimensional. Technical SEO, UX performance, entity coverage, author transparency, and conversational formatting will blend into a unified signal matrix.
Instead of chasing SERPs, SEOs will engineer content ecosystems tailored to AI comprehension—from entity graphs to passage-level relevance. This evolution isn’t speculative. It’s already visible in how Google positions websites within AI-generated summaries: based on what’s accurate, trustworthy, and grounded in real expertise.
Action Checklist: Get Your Content AI-Overview Ready
Bringing your content into Google's AI Overviews requires precise alignment with semantic principles, technical execution, and deep topical relevance. Use the following checklist to ensure your pages meet the core readiness criteria for AI-powered visibility.
 Optimize for Entity Recognition
Optimize for Entity Recognition
Embed clear, unambiguous references to named entities — people, organizations, places, products — using consistent nomenclature. Google’s AI processes entities with support from knowledge graphs like Wikidata, so reinforce connections with internal links to canonical sources and explicit context descriptions. Include disambiguation if an entity has multiple meanings.
 Verify Structured Data Implementation
Verify Structured Data Implementation
Scan your pages using tools like Google’s Rich Results Test and Schema.org validator. Apply relevant, specific schema types — Article, Product, FAQ, Person, Organization — and populate required and recommended properties. Use JSON-LD format for maximum compatibility and flexibility.
 Strengthen E-E-A-T Signals
Strengthen E-E-A-T Signals
Boost Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trust by auditing your author bylines, credentials, and backlink profile. Link to authoritative citations. Include first-hand insights, especially for YMYL topics. Profile your authors explicitly with schema (Person) and reference bios, interviews, or external publications.
 Align Content with User Intent
Align Content with User Intent
Analyze query types using tools like AlsoAsked, Semrush, and Google’s own “People also ask.” Outline informational, transactional, or comparative purposes, then structure headers and subsections to follow the user’s logical journey. Don’t just match keywords — fulfill the implied question underneath each search term.
 Add Semantically Related Subtopics
Add Semantically Related Subtopics
Expand coverage by integrating related concepts, co-occurring terms, and latent topics. NLP APIs like IBM Watson NLU or Google Cloud Natural Language can extract semantically connected terms from competitors’ top-ranking content. Bake these clusters into your content naturally — not as keyword stuffing, but as ontological coherence.
 Ensure Core Web Vitals Green Scores
Ensure Core Web Vitals Green Scores
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Target under 2.5s by controlling image delivery and server response times.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Keep shifts below 0.1 through visual stability — preload fonts, size images properly.
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Replace old FID benchmarks; stay under 200ms by optimizing script execution.
Run PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse audits routinely. Mobile performance takes precedence — Google indexes mobile-first.
 Track AI Overview Placements
Track AI Overview Placements
Currently, Google Search Console doesn't display AI Overview results within performance reports. Instead:
- Use rank trackers with AI Overview detection, such as SE Ranking or BrightEdge.
- Perform manual checks using incognito searches of target queries and observe AI-generated summaries.
- Capture versions across time using tools like Wayback Machine or automated screenshot scripts to monitor inclusion patterns.
Every item checked off this list pushes your content closer to being selected as an authoritative source for Google’s AI-led answers. Optimize strategically, publish intentionally, and track iteratively.
Move Now, Lead Tomorrow: Seize the AI Overview Advantage
SEO's foundations have shifted. The question isn't whether AI is changing search—it already has. Visibility now favors depth over density, meaning over matching, and context over keywords.
Ranking success today depends on how well your content aligns with Google's new AI-powered parsing of relevance. Structured data, entity clarity, and natural language aren’t optimization accessories—they're entry requirements. Those who restructure early don't just stay visible, they dominate the fold.
Revisit your most valuable content. Don’t skim it—analyze it. Ask:
- Does this page answer real, nuanced user questions as phrased in natural language?
- Is its context clear to an AI parsing for semantics and linked entities?
- Have I implemented schema markup that details what this page is about?
- Does this content communicate trust through firsthand expertise and demonstrable accuracy?
Run that audit today. Choose the page that brings the most traffic—or the one that should, but doesn’t—and apply the AI-Overview Optimization Framework.
Ready to compete in this new landscape?
Content ideas
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]
About us and this blog
We are a digital marketing company with a focus on helping our customers achieve great results across several key areas.
Request a free quote
We offer professional SEO services that help websites increase their organic search score drastically in order to compete for the highest rankings even when it comes to highly competitive keywords.
Recent Posts
View all projectsMore from our blog
See all postsRecent Posts
- How to Promote Last-Minute Black Friday Deals with SEO, AIO Search Fast With Online Advantages November 21, 2025
- The AI Overview Detective: How to Confirm Your Featured Status September 10, 2025
- Google Ads: Take Back Control of Your Online Experience September 10, 2025